Biology

Flies belong to the order Diptera, meaning “two wings.” Unlike most insects, they have only one pair of wings, making them agile fliers.
There are over 110,000 fly species worldwide, with major types commonly found in Canada:
- House Flies
- Cluster Flies
- Blow Flies
- Bottle Flies
- Drain Flies
- Fruit Flies
Flies are drawn to homes and businesses in search of food, moisture, and waste. They breed quickly and are known carriers of bacteria and disease, contaminating surfaces wherever they land.
Because they pose health risks and multiply fast, professional fly control is essential to protect your home or business.
Species like house flies and fruit flies are known to spread cholera, dysentery, typhoid, and other dangerous bacteria.

- A single female house fly can lay up to 500 eggs, hatching into thousands of flies within days.
- Thanks to tiny lenses called ommatidia, these compound eyes allow flies to see behind them 360 degrees at once. Making it hard to sneak up on them.
- Flies can beat their wings up to 1,000 times per second. This super-fast wingbeat lets them hover and dart in milliseconds.
- Flies can taste with their feet, when they land on food, they’re literally tasting it through their tiny feet.
- Flies carry over 100 deadly pathogens, including bacteria that cause cholera, typhoid, and dysentery.
Behaviour, Habitat & Diet

Behavior
Flies are persistent, fast-moving pests that actively seek out food, warmth, and moisture. They detect food odors from garbage, drains, and even air currents, quickly entering homes through open doors, windows, and vents. Some species, like cluster flies, also seek indoor warmth on cooler days and cooler air on hot days, making your property a year-round target.
Habitat
Flies typically breed outdoors in manure, garbage, compost, and animal carcasses, but many also reproduce indoors in:
- Kitchen drains
- Garbage bins
- Overripe fruit
- Damp mops or sponges
- Pet waste areas
They rest on ceilings, light fixtures, walls, and windows, especially near food sources or temperature-controlled spaces.
Diet
Depending on the species, flies feed on a wide range of organic matter, including:
- Rotting food and produce
- Meat and greasy residues
- Animal waste
- Sweet liquids and fermenting substances
House flies vomit digestive enzymes onto solid food to break it down before ingestion, increasing the risk of contamination.
Flies pick up pathogens from filth like trash, feces, and dead animals; and transfer them to surfaces, food, and prep areas.
Life Cycle
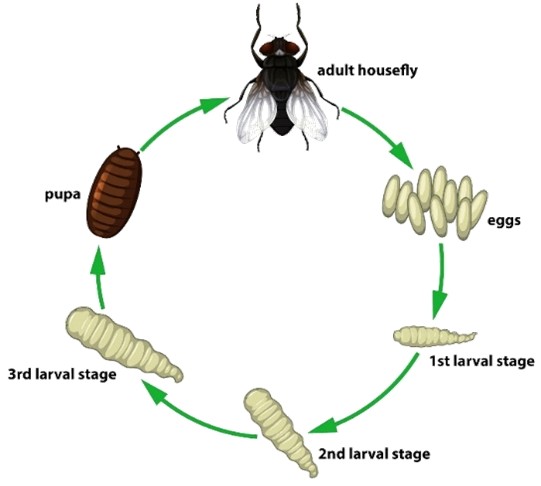
Flies reproduce rapidly through a four-stage cycle.
Egg:
- Females lay up to 500 eggs in moist, organic matter like garbage, manure, or drains.
- Eggs hatch within 24 hours.
- Maggots feed and grow rapidly.
- Maggots go through 3 active growth stages, called instars.
- After a few days, larvae enter the pupal stage, transforming in a protective casing.
- Adult flies emerge ready to reproduce.
- Completing the cycle in as little as 7–10 days.
Larva Stage
Pupa Stage
Adult Stage
One female house fly can lay up to 500 eggs, with new adults emerging in just 7–10 days, quickly turning into hundreds swarming your home within days.
Don’t Let Flies Buzz Around Your Home And Threaten Your Family’s Health.
Call Eradicare now! Our expert team hunts down every hidden breeding spot and delivers eco-friendly treatments that wipe out flies for good.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT FLIES
Flies are more than a nuisance, they spread over 100 harmful bacteria, including E. coli and salmonella, just by landing on food, utensils, or surfaces. Fast breeding means one fly today could be hundreds by next week.
Common indoor invaders in Canada include house flies, fruit flies, drain flies, cluster flies, blow flies, and bottle flies. Each species has different habits and hiding spots. Eradicare identifies and targets the exact cause.
Most DIY sprays and traps offer only temporary relief. They rarely address hidden breeding sites or eggs, leading to constant reinfestation. Professional treatment targets the entire life cycle for lasting results.
Flies are drawn to food odours, garbage, drains, compost, and even tiny food spills. Warmth, moisture, and poor sanitation make your space a perfect breeding ground.
Very fast. A single female can lay up to 500 eggs, and new adults can emerge in just 7–10 days. Infestations often explode before you notice a problem.
Our certified technicians conduct a thorough inspection, locate breeding sites, and apply targeted treatments, inside and out. We also create preventive barriers to stop future infestations.





