Biology

Bedbugs, members of the Cimicidae family, primarily Cimex lectularius, are stealthy, nocturnal pests that hide in tiny crevices, making them hard to detect and eliminate without professional help.
- Size: 4 to 5 mm long (adults).
- Colour: Reddish-brown with a darker abdomen if blood has been digested.
- Description: Miniscule insects with an oval shaped flat body, two antennae and six legs.
- Order/Family: Heteroptera/Cimicidae.
- Scientific Name: Cimex Lectularius.
Once inside, bedbugs establish a breeding ground and multiply rapidly, leading to sleepless nights and emotional distress.

- Bed bugs feed for 5–10 minutes, injecting anesthetics and anticoagulants to avoid waking the host.
- They spread easily by hitchhiking on luggage, clothing, and personal items.
- Their small size and ability to hide in cracks make them hard to detect.
- Bites can trigger allergic reactions or lead to infections from scratching.
- One pregnant female can start a full infestation within weeks.
- Heat treatments above 113°F (45°C) are effective for extermination.
Behaviour, Habitat & Diet

Behaviour
Bed bugs are nocturnal, feeding on blood at night and hiding during the day. Attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide, they move quickly and reproduce fast, often going unnoticed until infestations grow large.
Habitat
They hide in small, dark spaces near sleeping areas, including:
- Mattress seams and furniture.
- Cracks in walls and floors.
- Behind baseboards, wallpaper, and outlets.
- Inside luggage and clothing.
Diet
Bed bugs feed only on blood from humans and animals. Their bites can cause itching, allergic reactions, and stress. Even a few bites may signal a larger hidden infestation.
When a bed bug feeds, its body noticeably expands—from approximately 4–5 mm (about the size of an apple seed when unfed) to roughly 7–9 mm long once fully engorged, swelling into a plump, football-like shape.
Life Cycle
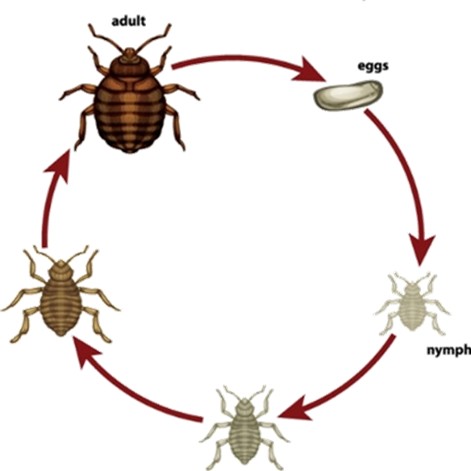
Bed bugs undergo a gradual metamorphosis. Their three life stages are egg, nymph and adult.
Egg Stage
- Females lay 200–500 eggs in their lifetime.
- Eggs are tiny (about 1 mm), white, and sticky.
- Hatch in 6–10 days.
- Newly hatched nymphs are pale and about 1.5 mm long.
- Go through 5 molts (shedding skins) to reach adulthood.
- Require a blood meal before each molt.
- Develop into adults in 5–7 weeks under ideal conditions.
- Adults are reddish-brown, oval-shaped, and about 5–7 mm long.
- Can live several months, and up to a year in cooler conditions.
- Females can start laying eggs shortly after mating and feeding.
Nymph Stage
Adult Stage
Once a colony is established, simply removing visible bed bugs won’t stop the infestation. The hidden females continue to lay eggs, allowing the problem to worsen.
Act Now To Experience Peacefull Nights with Eradicare’s Bed Bug Solutions
Don’t Let Bed Bugs Win! Call Eradicare today! Our experienced exterminators will assess your situation, implement a targeted solution, and ensure your property is protected from future invasions.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BED BUGS
Bed bugs are active year-round, but they become more prevalent in warmer months, especially when people travel.
While not known to transmit diseases, bed bug bites can cause intense itching and allergic reactions, affecting your well-being.
Bed bugs can enter your home through infested furniture, luggage, or clothing and thrive in overcrowded living conditions.
Contact Eradicare for a professional inspection and treatment. Avoid moving items from the infested area to prevent spreading.
Spraying can help but may not eliminate all bed bugs and eggs. A comprehensive approach is often required for complete eradication.
Costs vary based on the infestation’s severity and treatment methods. Eradicare offers competitive pricing and provides detailed estimates after inspections.
Our treatment includes thorough inspections, targeted extermination techniques, and preventative measures to ensure complete elimination of bed bugs.
